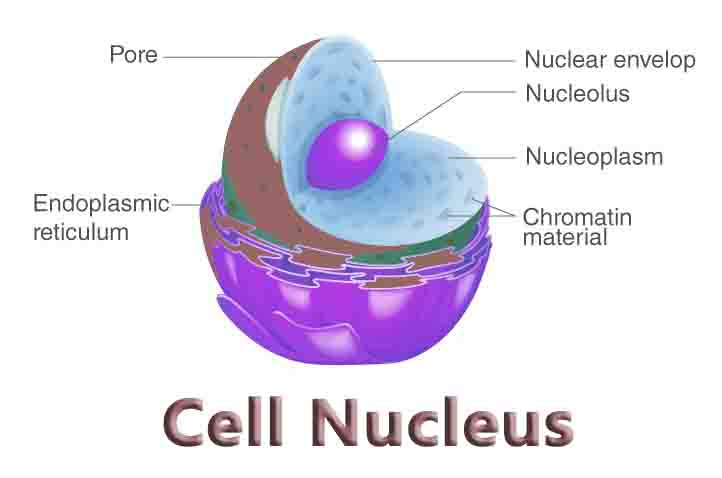
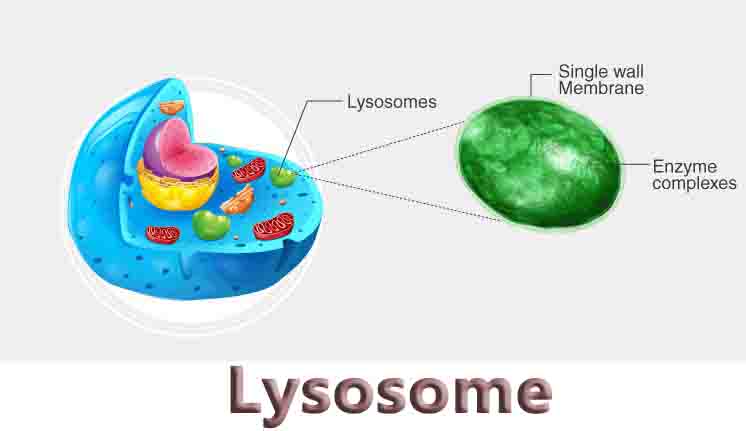
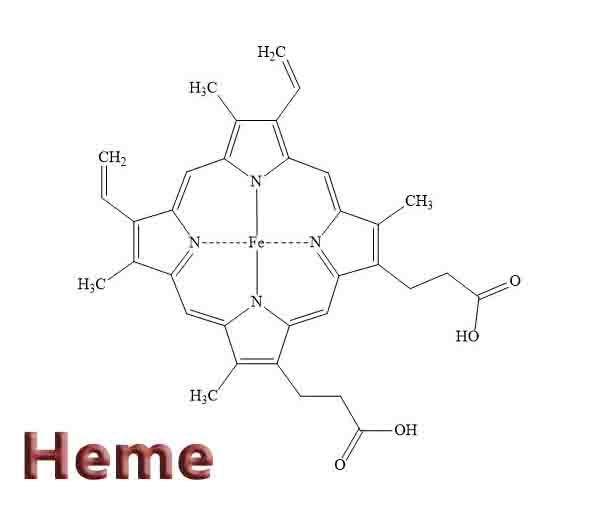
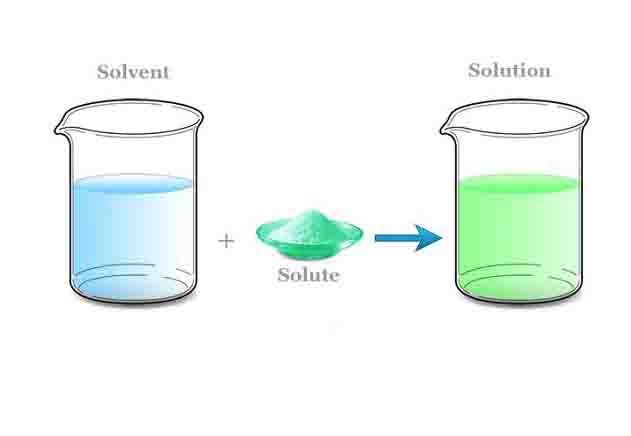
Small business ideas for women and men that are low-cost and high-profit
Want to start a small business but don’t want to work for someone else? Yeah, you’re in luck! I’m going to share some small business ideas that don’t require a lot of investment but offer high profits. No matter what you’re looking for, there are plenty of opportunities for you to explore and succeed, whether … Read more